What are the Three Pillars of Sustainable Development?

Have you ever heard about sustainable development or the three pillars of sustainable development?
👉 Maybe so, but do you know what are the three pillars of sustainability you must know in order to successfully implement this concept in your company?
Let's take a look together.
What is sustainable development?
The concept of sustainable development is named after the Brundtland report, which reported sustainable consumption in developed countries.
Sustainable development is based on three fundamental pillars: social, economic and environmental.
The Brundtland report, which sustainable development is gets its name from – delineated the development of human resources in form of extreme poverty reduction, global gender equity, and wealth redistribution.
👉 The Brundtland report was imperative to implement strategies to prevent environmental degradation, and how environmental limits impact energy efficiency, the global economy, economic resources, and overall sustainable industrialization and development.
The definition of sustainable development according to the Brundtland Report
The Brundtland Report was drawn up as part of the UN World Commission on Environment and Development in 1987.
This over 300-page document aimed to shape national policies and sets out the key measures to be integrated in order to protect the planet and human life. Although this report on the technological process of sustainable development is titled, “Our Common Future”, it is often referred to as the “Brundtland Report” after Gro Harlem Brundtland, Prime Minister of Norway at the time and Chair of the commission.
The concept of sustainable development was explained in depth in this report through the discussion of climate change, economic development, and global goals that should be implemented in order to achieve sustainable development.
The term “sustainable development” was initially incorrectly translated in French as “développement durable”. However, sustainable development refers to how to sustain development for current and future generations, rather than how to create resilient infrastructure. The translation of sustainable development was corrected in later editions of the document to “développement soutenable”. However, the initial translation of sustainable development is the more commonly used phrase in French when referring to sustainable development.
The definition is as follows:
Sustainable development is development that strives to meet the needs of developing countries seeking to achieve a more sustainable world. Sustainable development addresses the needs of the present moment without compromising current and future generations to meet their own sustainable lifestyles.
Sustainable development can be applied to corporate policy in the business world as it encompasses three key areas: economic, environmental and social. Sustainable development requires that a company must contribute to economic growth, social progress and promote environmental sustainability. The three key areas of sustainable development cane be ranked in the following order of importance, environmental conservation, economic development, and social sustainability.

What are the three pillars of sustainable development?
Social pillar
The social pillar of a company's sustainable development refers to values that promote equality and respect for individual rights. The social consequences of the company's social activity are then assessed in accordance to these issues, such as gender equality.
The principles upon which this pillar is founded are as follows:
- Combat social exclusion and discrimination: helping with reintegration, supporting gender equality, reducing the gender pay gap, promoting training, encouraging dialogue, and applying global social rights. In other words, the goal is to seek to aid the global population.
- Promote solidarity: helping to reduce social inequalities by collaborating with local and international associations and projects, and prioritizing fair trade products which guarantee an appropriate income for farmers and help to promote sustainable agriculture.
- Contribute to the well-being of stakeholders: developing social dialogue, encouraging the exchange of information and transparency, adapting working hours according to employee profile, and making premises accessible to people with reduced mobility.
Economic pillar
This pillar is based on companies’ ability to contribute to economic development and growth. In other words, they must encourage and promote the protection of the environment by limiting the risks posed by their production. The recycling of products and the use of renewable energy are therefore fundamental aspects of the development of the economic pillar.
Furthermore, the ISO 50001 standard which is focused on energy efficiency, aims to improve energy performance, with a view to reducing energy consumption and therefore contributing to economic growth. Effectively implementing of this standard leads to a certification, serving as a guarantee of optimal, affordable and clean energy use.
Environmental pillar
The environmental pillar is founded on a commitment to protect the environment by reducing risks and measuring the environmental impacts of companies' activities.
The challenges for companies in this area are as follows:
- Saving and preserving natural energy or agricultural resources
- Assessing their carbon footprint and reducing total greenhouse gas emissions and further achieve sustainable development goals.
- Prevent water scarcity and reduce overall waste for current and future generations.
Companies must set targets to improve their performance on environmental issues. These goals are an integral part of Corporate Social and Environmental Responsibility (CSER).

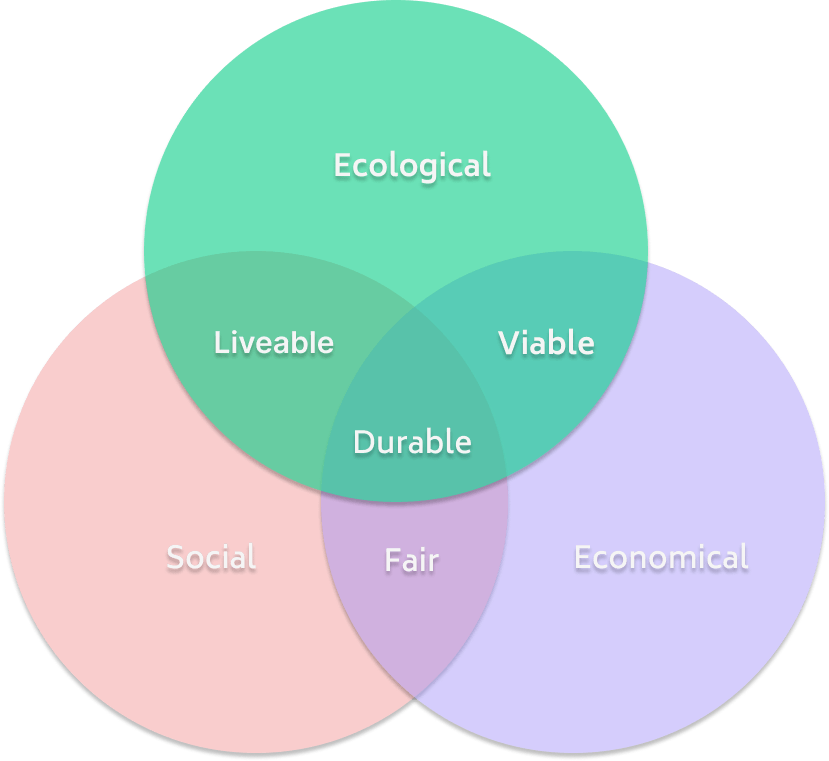
Diagram of the three pillars of sustainable development: what is it?
The three pillars of sustainable development can be illustrated using a diagram to provide a clearer understanding of the greatest challenges facing humanity involved and how they impact one another.
Why is a fourth pillar sometimes mentioned?
A fourth pillar is often acknowledged as a sustainable pillar or culture. For instance, culture can refer to the difference in sustainable lifestyles and carbon emissions in various places : such as New York or a small island developing states.
Though it is often not recognised as a core pillar to achieving sustainable development, culture is an important part of sustainable development since it incorporates all three of the fundamental aspects of sustainable development described above.
Culture: a basic but central element of sustainable development
The Brundtland Report delineated how economic growth, social inclusion and environmental balance are essential to create a sustainable development solutions network – utilizing local, national and global development strategies.
However, these aspects alone cannot account for the full complexity of our current societies.
Organizations and events such as UNESCO or the World Summit on Sustainable Development (2002) have since advocated for culture to be included in this model. Culture is a complementary factor as it shapes our meaning of “development” and determines the actions of communities around the world.
The UNESCO Universal Declaration on Cultural Diversity (2001) and the Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (2005) define the relationship between culture and sustainable development in two specific ways:
- The development of the cultural sector in itself and its economic dimension (cultural heritage, creative and cultural industries, crafts, cultural tourism, etc.);
- The notion that culture plays a clear role place in all public policy, such as in united nations – including that related to education, economy, science, communication, environment, social cohesion and international cooperation.
👉 However, the world is not only facing economic, social and environmental challenges. Creativity, knowledge and diversity are all key elements for creating a conversation to promote peace and social progress. These values are intrinsically linked to the ideals of human development and freedom.
The world’s cultural challenges are too complex to be considered in the same manner as the other three original aspects of sustainable development. This fourth pillar is strongly linked with the other three dimensions of sustainable development, and is complementary to each of them.
Culture is thus a driver of social values (cohesion, solidarity, fundamental freedom, human settlements, etc.), it contributes to global economic sustainability and is as important as the environment to humankind because of the heritage it represents.
Why integrate culture into the pillars of sustainable development?
As previously discussed, culture should be integrated into the pillars of sustainable development predominantly because it encompasses social and economic dimensions. But that is not the only reason, culture can also be employed as an effective strategy to support the three fundamental pillars. It plays a socially-binding and facilitating role in the face of economic, societal and environmental challenges.
Furthermore, the culture of sustainable development (its foundations, its history, its evolution) is often overlooked within companies. More importantly, raising awareness of this culture would provide a better understanding of the issues at stake when implementing management policy (particularly in terms of corporate social responsibility) and encourage greater involvement: such as to eradicate poverty, ensure access to one's own needs to young people, and to provide under-developed countries with basic services that could help to mitigate climate action or decrease the emission of fossil fuels.
Finally, culture can have a positive impact within a company insofar as it unifies and consolidates human activities and remains an essential element of the company's overall dynamic.
"The set of distinctive spiritual, material, intellectual and emotional features of society or a social group, that encompasses, not only art and literature but lifestyles, ways of living together, value systems, traditions and beliefs.”– UNESCO
👉 Therefore, it could be said that sustainable development is not defined by three fundamental pillars, but through four major dimensions: social, economic, environmental and cultural.
Why apply these pillars within your company?
The approach of implementing these four pillars of sustainable development within your company can only be beneficial for the smooth running of your business and for adopting a responsible management policy (CSR).

Social pillar: ensure the well-being of your employees
Governance that conveys social values is conducive to the well-being of your employees and associates. A company is more likely to prosper if its employees feel happy in their work. They will certainly stay with the team longer and the work dynamic will be better.
👉 For a company, taking ethical action means implementing a reference model of good practices for a more virtuous society. Therefore, the social pillar plays a critical role in achieving sustainable development.
Economic pillar: optimise your budget
Adopting a more responsible approach to production by encouraging recycling, limiting waste and using renewable raw materials can considerably reduce your current expenditure while still promoting sustainable consumption. Better resource management and the integration of waste into a second line of production or sales channel are good practices for optimizing your budget and natural resources.
👉 The economic pillars plays a key role in sustainable development as it opens more doors for success in the other pillars of sustainable development.
Environmental pillar: improve your CSR strategy
Integrating environmental targets into the management of your company is essential from a corporate social responsibility (CSR) perspective. Already a legal obligation for companies with over 500 employees, a CSR strategy is also recommended for other businesses that want to invest in an eco-friendly way while improving their brand image.
👉 The environmental pillar is imperative as it creates a more sustainable world for future generations, and overall helps to mitigate climate change.
Cultural pillar: boost cohesion and support among stakeholders
Integrating the cultural role is an essential component of any company. As a unifying force, culture helps to build real social ties, which result in more dynamic exchanges, better group work and, therefore, an increase in the productivity of your employees. Moreover, culture boosts motivation and education through intellectual stimulation.
Overall, the cultural pillar of sustainable development plays a crucial role the individual performance of your company's stakeholders.
Some practical examples of applying these three pillars in companies
Greenly has provided below some examples of practical actions that can be taken for each fundamental pillar in order to help you understand and implement the many processes needed to achieve sustainable development practices within your company.
Social pillar
- Encourage remote working: remote working is becoming increasingly popular with employees who want to better organise their personal and professional life. This method of working helps to reduce stress and increases employee productivity.
- Integrate the SDGs into your CSR strategy: the Sustainable Development Goals set by the UN to address global challenges include actions such as helping to provide education children or the fight to ending poverty.
- Promote training and access to employment: organizing an in-house training and offer access to employment for people in socially vulnerable situations is a great step to achieve sustainable development.
Economic pillar
- Review your energy consumption: conducting a carbon assessment as part of your CSR strategy will provide precise metrics on your company's energy consumption. This is an effective way to target the areas where efficiency needs to be improved in order to establish a more sustainable world for future generations.
- Renovate and insulate your buildings, as most buildings are poorly constructed and/or insulated. This is a major source of energy loss, and technological progress in more effective machinery can help promote sustainability and converse energy resources.
Environmental pillar
- Ensure better waste management: sort waste and promote “zero packaging” as much as possible.
- Opt for green energy: switch to a renewable energy provider (solar, wind, hydropower, etc.).
- Implement a more eco-friendly travel plan: such as running a company shuttle service to prevent your employees from using their own vehicles is a good way to combat climate change.
Cultural pillar
- Organise evening events: this is ideal for strengthening social bonds within your teams.
- Issue vouchers for cultural activities: such as action to promote cultural events is always popular with employees.
- Found a company sports association: creating a sports group among your company's stakeholders is an American trend that is becoming increasingly popular in France. Not only is it a fun co-working activity, but it promotes team spirit and solidarity.
What about Greenly?
If reading this article about the three pillars of sustainable development has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
Trying to manage the three pillars of sustainable development is difficult, but don’t worry – Greenly is here to help. Click here to schedule a demo to see how Greenly can help you find ways to improve energy efficiency and decrease the dependency on fossil fuels in your own company.
Greenly can help you make an environmental change for the better, starting with a carbon footprint assessment to know how much carbon emissions your company produces.


Green-Tok, a newsletter dedicated to climate green news
We share green news once a month (or more if we find interesting things to tell you)





