Are Oceans Turning Green Because of Climate Change?
In this article, we’ll explore the reasons behind the changing colors of the oceans, discuss what this means for marine life, and determine how these shifts reflect larger environmental changes.
Your request has been taken into account.
An email has just been sent to you with a link to download the resource :)

It’s a fact: most of our actions have an impact on the environment. Commonly called the "ecological footprint", this indicator is the result of a true ecological awareness. As it is, our lifestyle and daily activities are far from being harmless for the planet. The proof is in the pudding: the day of the climate action deadline advances a little more each year. On July 29, humanity consumed all the resources that the Earth is able to regenerate in one year. The cause? The pressure that Man exerts on the environment. What is it due to? What is the ecological footprint? How can it be calculated? Greenly will tell you all you need to know.
Everything you need to know about the ecological footprint.
The ecological footprint (also called "environmental footprint", is an indicator developed by the Global Footprint Network.It measures the impact of Man on the environment, by determining the amount of raw materials consumed and the amount of harmful substances (or greenhouse gasses) generated, then released into the atmosphere.
In short, the more we consume, the more resources we use and the more we pollute.
The environmental footprint is calculated in terms of the number of planets or land area (global hectares). It determines how much space is needed to support our needs, given our lifestyle.
This calculation can be done on an individual, national or planetary scale.
For example:
The conclusion is clear: we are overexploiting the Earth's resources. To such an extent that nature has more and more difficulty to regenerate itself.
Is there a note of hope in this gloomy picture? We are, in fact, able to reverse the trend by changing our behavior!

Our food, our housing (in terms of surface and energy), our consumption habits or our modes of transport have an impact on the environment. In other words, our daily life itself is likely to pollute, because we are not aware of the environmental impact of some of our choices. This being said, some areas are obviously more harmful than others (the choice of our means of transportation, in particular).
In short, the ecological footprint is the ratio between consumption and biocapacity (i.e. the earth’s ability to produce the resources we are demanding from it).
Note: the overexploitation of resources and the waste produced by humans have serious consequences on the planet, and on its mechanisms (regeneration of natural resources, absorption and rejection of waste, etc.).
Be careful not to confuse carbon footprint and environmental footprint.
These two calculation methods have in common that they raise awareness of one's environmental impact (one's CO2 emissions, in particular), as well as the need to start a real energy transition.
Nevertheless, these two footprints do not reflect the same information:
To adopt sustainable behavior, it is important to take stock beforehand. After all, how can you change your lifestyle, without knowing what aspects of it could be improved? This is where the calculation of the ecological footprint makes sense.
The Global Footprint Network determines the exact date of the Overshoot Day, based on the environmental footprint on a national and/or global scale.
In short, this is the date from which the planet's annual resources are exhausted.
Note: as of Overshoot Day, we also exceed the amount of GHGs that our ecosystem is able to naturally eliminate in one year.
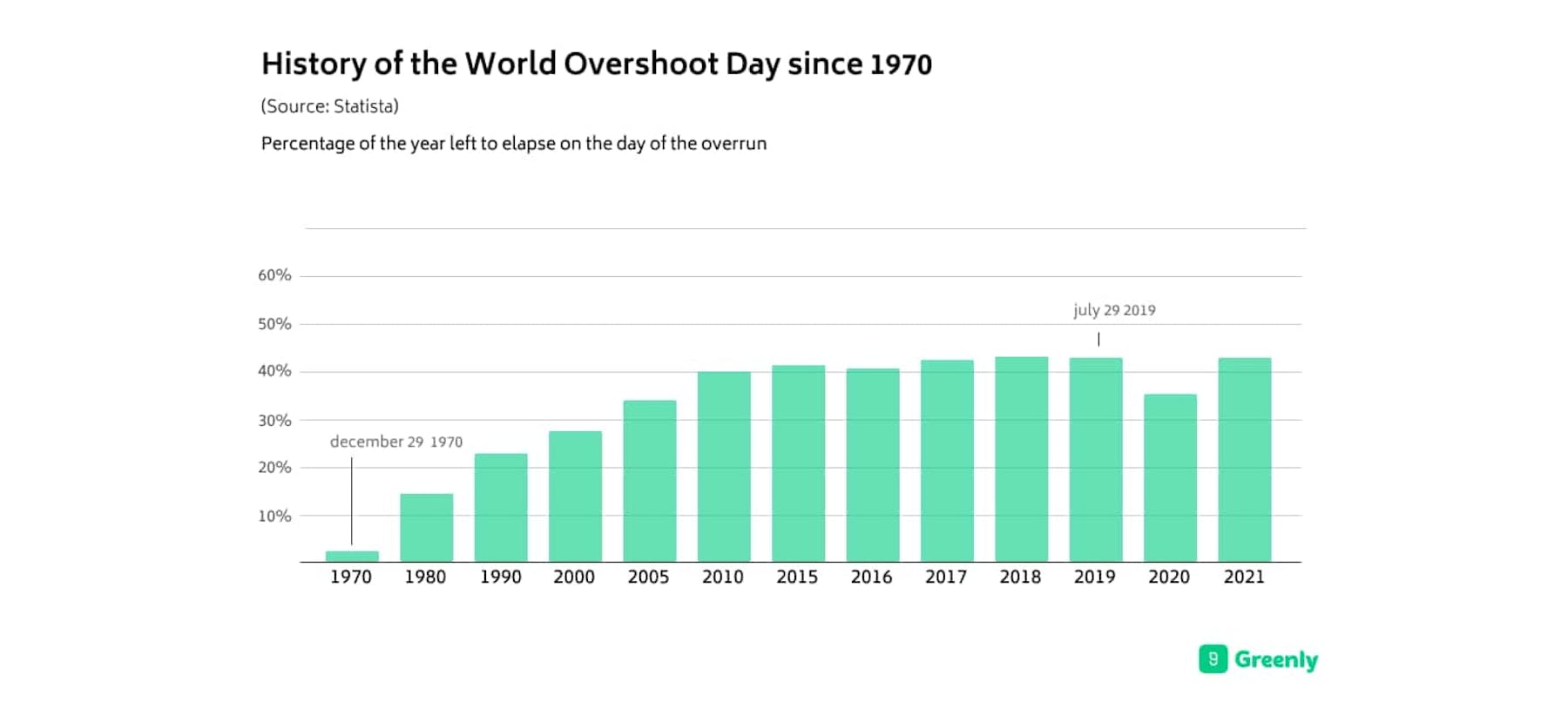
For several years, we have been talking about an ecological deficit, since our environmental impact exceeds the planet's biocapacity. Moreover, this date comes earlier and earlier, as time goes by (July 29, 2021, August 20, 2020, etc.). From midsummer on, humanity is living on credit.
At the level of a country as well as a company, the calculation of the environmental footprint thus allows us to identify bad practices. Where the latter allows (in the first case) to contribute to the creation of a sustainable society model, it allows a brand to work on the development of a more sustainable business model as well.
This suggests a more fair sharing of resources and wealth.
There are several environmental footprint calculators. These tools usually take the form of a questionnaire divided into several parts: food, place of living, modes of transport used, etc.
According to the answers provided, the tool determines the GHG emissions generated by these consumption habits, and then suggests some areas of improvement intended to promote the transition to a more ecological lifestyle.
Examples include the Global Footprint Network calculator, the ADEME calculator and the wwf calculator (based on Swiss averages).
It is possible to contribute to reducing the global ecological footprint, by making targeted individual changes. So: how can you reduce your impact on the environment? Here are our eco-tips.
This first point is surely the most important, since it is one of the main contributors to the ecological footprint.
Did you know that the transportation sector is responsible for 31% of French GHG emissions (High Council for Climate report 2019)?
Unsurprisingly, airplanes and diesel (or gasoline) cars are the most polluting modes of transportation.
Faced with this observation, it is advisable to try to "move smart", by giving priority to cycling, walking and public transport (metro, bus or train).
If it is impossible to leave the car in the garage, carpooling and the electric car are interesting alternatives to limit CO2 emissions.
Does this mean that we should give up flying? No, in fact, some trips to distant countries leave no other alternatives. In this case, there is no need to kick ourselves. It is quite possible to compensate for the CO2 emitted during this trip: simply study the aspects of your daily life on which you could make valuable GHG savings, before and after your trip.

Here, the advantage is twofold: in addition to acting for the planet, you save on your bill!
This happens, first of all, by reducing the environmental impact of your heating and cooling.
According to WWF, electric boilers emit 10 to 12 times more GHGs than solar panels, photovoltaic installations or heat pumps. In addition, electric heating wastes 6 times more energy than a heat pump.
In order to reduce their energy consumption, homeowners can invest in the installation of new equipment, giving priority to the use of renewable energy. Tenants can send a letter to their landlord to request the installation of a green alternative and good thermal insulation.
On average, the temperature of unused rooms should be lowered by 2 or 3 degrees (compared to what is done today) and living rooms should be heated to no more than 21 degrees.
One more thing? Water consumption is not left out! Roughly speaking, we individually use the equivalent of 150 liters of water per day (washing machine, shower, toilet flush and dishwasher).
So use water wisely by not leaving the tap running when brushing your teeth, for example. Take showers instead of baths and don't run the machine half empty.

According to Eurostat, the volume of waste continues to increase in Europe. France produced 546 kg of garbage per capita in 2021.
Our advice?
In France, the environmental impact of our food represents between 20 and 50% of our ecological footprint, reveals ADEME.
In order to reduce this rate, we need to rethink our consumption on an individual scale.
A little tip: foods marked "best before" can be eaten a few days after the expiration date.
In the same way, consuming in a sustainable way implies the adoption of certain good practices:
As a reminder, going from 2 kg to 300 g of meat per week allows you to save 1 ton of CO2 per year. In concrete terms, reducing one's environmental footprint is simply a matter of adopting responsible behavior, by consuming better and buying sensibly.
The rebound effect (also known as Jevons' paradox) is a particularly frustrating paradox. There are two types: the direct effect and the indirect effect.
In the first case, the efforts made lead to disastrous results. This is the case, for example, when we over consume an alternative initially considered better than the initial solution.
The most popular example concerns the use of LED bulbs: given their low environmental impact, consumers tend to leave them on excessively. The result is that this neglect negates all the efforts made, causing an even more negative impact than the original problem.
In the second case (the indirect rebound effect), a series of good practices is adopted, the results of which are then totally canceled out by a given action. This can be the case if you make efforts on your daily energy consumption before buying a diesel car, for example.
If reading this article about ecological footprint has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
At Greenly we can help you to assess your company’s carbon footprint, and then give you the tools you need to cut down on emissions. Why not request a free demo with one of our experts - no obligation or commitment required.


We share green news once a month (or more if we find interesting things to tell you)